- Food Science
-
by k.mammasis
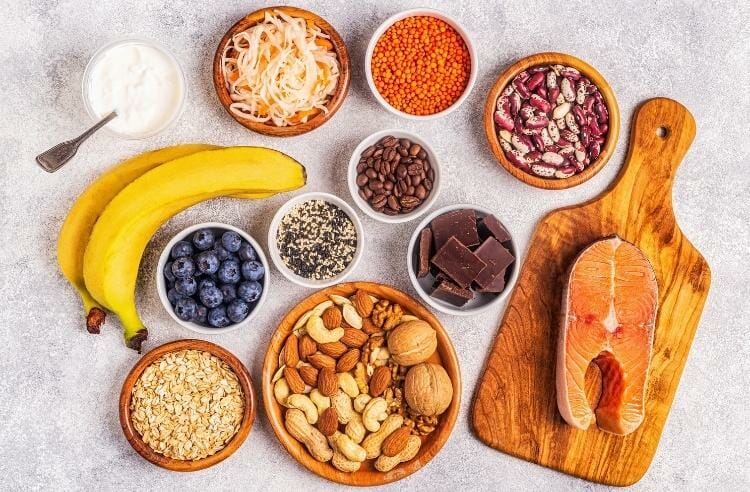
It is critical to ingest omega-3 fatty acids. When received from foods instead of supplements, these necessary components of your cell membranes, are ideal for treating your omega 3 deficiency. They are required by your body to create signaling molecules known as eicosanoids, which aid in the proper functioning of your neurological, immunological, cardiovascular, and endocrine systems. Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), as well as their essential precursor alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), are important omega-3 fatty acids found in high amounts in functional foods. An omega-3 deficiency occurs when your body does not receive enough of those omega-3 lipids. This could have a harmful impact on your health. This article discusses the most commonly met signs and symptoms of omega-3 deficiency, how to know if you have a low omega-3 status, and how to raise your omega-3 fatty acid consumption through functional food.
At MILESTONE®, we strictly select the best natural formulations and avoid synthetic ingredients. We have developed a range of functional foods that will get you filled only by consuming 10ml of each product. Our unique High Phenolic Olive + Algae Vegan Omega 3 Oil (EPA DHA ALA) has an ideal omega 6 to omega 3 ratio (1.5:1) and contains natural EPA + DHA from algae, that. Alternatively, you may choose to begin with our pure medical olive oil, which is an ideal food for omega 3 6 and 9 + very high level of rare polyphenols. If you are looking into ways to enrich your plant-based omega-3 diet, then it would be great to read our article on the top vegan foods for omega-3.
Depression & Anxiety
Depression is one of the world’s most common mental illnesses in the 21st century. Omega-3 fatty acids are a necessary component for both the brain and heart, with multiple health benefits that extend as far as lifting the effects of depression. Many studies have found a link between low omega-3 levels and an increased risk of depression 1 2. One meta-analysis of 26 studies involving 2,160 people discovered that consuming omega-3 supplements improved depression symptoms 3. In addition, a recent study 4 5 also concludes that: “Those patients who may have depression because of insufficient omega-3 fatty acids can respond well to the diet containing high levels of omega-3 fatty acids and can show positive signs regarding treatment of depression. However, for patients who have depression due to factors other than omega-3 fatty acids diet, expecting that type of depression can be treated due to omega-3 fatty acid supplement does not seem reasonable.“. Finally, in the following studies researchers have confirmed that when people suffering from depression or anxiety begin taking omega-3 supplements, their symptoms improve 6 7.
Skin Irritation and Dryness
First, let’s make clear that DHA is an important structural component of your skin. It is in charge of the health of cell membranes, which actually comprise the majority of your skin. In simple words, a healthy cell membrane results in skin that is smooth, moist, supple, and wrinkle-free. And this is what most of us would fight for retaining over the years of oxidative stress and damage.
One of the first places you may notice a deficiency of omega-3 fats in your body is in your skin. Omega-3 fatty acids increase the integrity of the skin by limiting moisture loss and protecting the skin from irritants that can cause dryness and irritation 8 9.
1. May protect against sun damage 10
2. May reduce acne 11 12
3 . May guard against dry, red, or itchy skin 13
4. May accelerate wound healing 14.
5. May boost hair growth and reduce hair loss15.
Dry Eyes
Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to eye health by preserving ocular moisture 16. For this reason, it is very common to see prescription medications that include omega-3 supplements in order to alleviate the dry eye syndrome and discomfort caused by it. It is important to know that DHA, an extremely important omega-3 fatty acid, is a structural component of your retina, so when you don’t get enough of it, vision problems may arise 17. You may read more on our recent article entitled Functional Foods for Omega 3 and how they will assist you in treating your omega 3 deficiency.
How to Test for Omega-3 Deficiency
It is uncommon for doctors and nutritionists to frequently assess an individual’s omega-3 status. But this habit is continuously changing and it becomes more and more common that your endocrinologist for example requests an assessment of your vitamin D status together with your TSH, FT3, or FT4 levels that concern your thyroid function. And all this with a simple and accurate blood test. To begin, your doctor can collect a blood sample and test omega-3 levels in blood fats or blood plasma, which are expressed as a percentage of total phospholipid fatty acids by weight. By measuring the fatty acid makeup of red blood cells, healthcare providers can indirectly determine omega-3 levels. This method examines long-term dietary fat intake over several months and may offer an estimate of overall omega-3 intake 18.
However, it is crucial to note that the amount of fatty acids in the blood might fluctuate greatly depending on when and what you ate last. This is why, in most cases, a person must avoid eating overnight prior to providing a blood sample for this specific analysis.
Food for Improving Omega-3 Status
Functional foods are your best natural shield for treating various omega-3 related deficiencies. In our recent article: 5 Foods With The Most Omega-3 Fatty Acids we provide a list of functional foods with the highest to lowest concentration of omega-3 fatty acids, among which you will find our unique combination of olive+algae for covering your omega 3 deficiency, seafood and hemp seeds. Go and have a look at these delicious functional nutrition tips!
The Perfect Functional Foods for Omega-3 Deficiency
The omega-3 lipid ALA can be found in a variety of foods, including chia seeds and other plant foods. DHA and EPA are found in fish and other animal-based meals. Each source has unique pros and cons, but there is no known plant-based source that combines all three in one profile. For this reason, we created a couple of plant-based functional foods that will cover all your needs, and they are also free of pesticides or any other contaminants.
1. High Phenolic Olive Omega 3 6 9
Among our best-sellers is our High Phenolic Olive Oil with plant based omega 3 6 9. An anti-oxidative stress food that is good for your heart and brain, it is abundant with Omega 3 (ALA), Omega 6 and Omega 9 (oleic acid) fatty acids, with natural hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol bioactive compounds. As a result, MILESTONE®’s highest polyphenol olive oil possesses at least 50 times more anti-oxidants than common olive oil and is the number 1 high phenolic olive oil product in pharmacies in Greece.
2. High Phenolic Olive + Algae Omega 3 Oil
Omega-3 content: 250 mg per 10ml (raw)
Omega-6 to Omega-3 ratio: 1.5:1
Plant-based sources of omega-3s usually just include ALA. Olive oil is possibly the greatest source of unsaturated fatty acids including a unique omega complex, i.e. ALA, Omega 6, and Omega 9. In addition, high-phenolic olive oil contains a unique set of bioactive compounds not found elsewhere in nature, e.g. tyrosol, hydroxytyrosol, and many more. On the other hand, algae oil is possibly the only exception to this rule, containing high amounts of EPA + DHA. In a recent study carried out by researchers at the University of Madrid, it was shown that treatment with a combination of olive oil and algae oil improved the lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, and vascular function in elderly rats while lowering aging-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver and cardiovascular system 19. We researched and developed a product that combines the unique attributes of our world-class medical olive oil with the ones offered by algae, in order to produce a synergistic combination of these great plant sources that offer unique health benefits to anyone in the look for substituting typical omega-3 supplements with functional food for omega-3s.
It is among the most natural and highly concentrated functional foods for omega 3 deficiency that we are aware of. And yes, it is among our top products because it has unparalleled qualities. It has no trace of chemical compounds or any form of toxification factors. Our formula supplies you with 250mg of the best food for omega-3 from algae (10ml / day), together with a set of bioactive compounds with pharmacological properties, e.g. oleacin, oleocanthal, oleuropein, elenolide. The concentration of olive oil polyphenols is among the highest in the world and always exceeds 500mg/kg. The olive oil polyphenols contained in our product will contribute to the reduction of your oxidative stress markers.
Summary
Omega-3 deficiency is a disorder in which your body lacks sufficient omega-3 lipids. While healthcare professionals do not routinely screen people for omega-3 deficiency, there may be some signs that your status is low. For example, dry and irritated skin, inflammation, hair thinning and loss, depression, dry eyes, and joint discomfort caused by inflammation.
Omega-3 fatty acids are necessary nutrients that can be better absorbed when received from foods than supplements. Food for omega-3 from algae and olive contains it all, DHA, EPA, and ALA. Algae oil provides an adequate amount of DHA and EPA and is sustainable and environmentally friendly as opposed to fish oil. Functional foods for omega 3 deficiency may safeguard heart health, boost cognitive performance, and reduce the risk of developing various chronic diseases.
A Word From MILESTONE®
MILESTONE® Food for your Genes uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
- Canhada S, Castro K, Perry IS, Luft VC. Omega-3 fatty acids’ supplementation in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. Nutr Neurosci. 2018 Oct;21(8):529-538. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2017.1321813. Epub 2017 May 3. PMID: 28466678.[↩]
- Grosso G, Galvano F, Marventano S, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids and depression: scientific evidence and biological mechanisms. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:313570. doi:10.1155/2014/313570[↩]
- Liao Y, Xie B, Zhang H, He Q, Guo L, Subramanieapillai M, Fan B, Lu C, McIntyre RS. Efficacy of omega-3 PUFAs in depression: A meta-analysis. Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Aug 5;9(1):190. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0515-5. Erratum in: Transl Psychiatry. 2021 Sep 7;11(1):465. PMID: 31383846; PMCID: PMC6683166.[↩]
- Wani AL, Bhat SA, Ara A. Omega-3 fatty acids and the treatment of depression: a review of scientific evidence. Integr Med Res. 2015;4(3):132-141. doi:10.1016/j.imr.2015.07.003[↩]
- Lin PY, Su KP. A meta-analytic review of double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007 Jul;68(7):1056-61. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v68n0712. PMID: 17685742.[↩]
- Su KP, Huang SY, Chiu CC, Shen WW. Omega-3 fatty acids in major depressive disorder. A preliminary double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2003 Aug;13(4):267-71. doi: 10.1016/s0924-977x(03)00032-4. Erratum in: Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004 Mar;14(2):173. PMID: 12888186.[↩]
- Ginty AT, Conklin SM. Short-term supplementation of acute long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids may alter depression status and decrease symptomology among young adults with depression: A preliminary randomized and placebo controlled trial. Psychiatry Res. 2015 Sep 30;229(1-2):485-9. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2015.05.072. Epub 2015 Jun 27. PMID: 26188642.[↩]
- Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Yassini-Ardakani M, Karamati M, Shariati-Bafghi SE. Eicosapentaenoic acid versus docosahexaenoic acid in mild-to-moderate depression: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013 Jul;23(7):636-44. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Aug 19. PMID: 22910528.[↩]
- Peter S, Chopra S, Jacob JJ. A fish a day, keeps the cardiologist away! – A review of the effect of omega-3 fatty acids in the cardiovascular system. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013;17(3):422-429. doi:10.4103/2230-8210.111630[↩]
- Pilkington SM, Watson RE, Nicolaou A, Rhodes LE. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: photoprotective macronutrients. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Jul;20(7):537-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2011.01294.x. Epub 2011 May 16. PMID: 21569104.[↩]
- Khayef G, Young J, Burns-Whitmore B, Spalding T. Effects of fish oil supplementation on inflammatory acne. Lipids Health Dis. 2012;11:165. Published 2012 Dec 3. doi:10.1186/1476-511X-11-165[↩]
- Jung JY, Kwon HH, Hong JS, Yoon JY, Park MS, Jang MY, Suh DH. Effect of dietary supplementation with omega-3 fatty acid and gamma-linolenic acid on acne vulgaris: a randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014 Sep;94(5):521-5. doi: 10.2340/00015555-1802. PMID: 24553997.[↩]
- Kawamura A, Ooyama K, Kojima K, Kachi H, Abe T, Amano K, Aoyama T. Dietary supplementation of gamma-linolenic acid improves skin parameters in subjects with dry skin and mild atopic dermatitis. J Oleo Sci. 2011;60(12):597-607. doi: 10.5650/jos.60.597. PMID: 22123240.[↩]
- Huang TH, Wang PW, Yang SC, Chou WL, Fang JY. Cosmetic and Therapeutic Applications of Fish Oil’s Fatty Acids on the Skin. Mar Drugs. 2018;16(8):256. Published 2018 Jul 30. doi:10.3390/md16080256[↩]
- Le Floc’h C, Cheniti A, Connétable S, Piccardi N, Vincenzi C, Tosti A. Effect of a nutritional supplement on hair loss in women. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015 Mar;14(1):76-82. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12127. Epub 2015 Jan 8. PMID: 25573272.[↩]
- Bhargava R, Kumar P, Kumar M, Mehra N, Mishra A. A randomized controlled trial of omega-3 fatty acids in dry eye syndrome. Int J Ophthalmol. 2013 Dec 18;6(6):811-6. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2013.06.13. PMID: 24392330; PMCID: PMC3874521.[↩]
- Lim LS, Mitchell P, Seddon JM, Holz FG, Wong TY. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet. 2012 May 5;379(9827):1728-38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60282-7. PMID: 22559899.[↩]
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/omega-3-deficiency[↩]
- González-Hedström D, Amor S, de la Fuente-Fernández M, et al. A Mixture of Algae and Extra Virgin Olive Oils Attenuates the Cardiometabolic Alterations Associated with Aging in Male Wistar Rats. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(6):483. Published 2020 Jun 3. doi:10.3390/antiox9060483[↩]